Elasticsearch实战:给博客打造全文检索
学习和使用Elasticsearch有一段时间了,项目中大量使用到了es,但对于我来说都是部分或者局部地去使用,所以得找个时间好好整理并且再完整实践一下es,于是就有了这篇文章。
首先系统架构是LNMP,很简单的个人博客网站(逐步前行STEP),
使用laravel框架,实现全文检索的引擎是elasticsearch,使用的分词工具是ik-analyzer然后是安装组件:elasticsearch/elasticsearch,以下列表是本次实践所用到的软件/框架/组件的版本:
- PHP 7.1.3
- Larvel 5.8
- Mysql 5.7
- elasticsearch 5.3
- elasticsearch/elasticsearch 7.2
以下默认上述环境已经准备完毕。
实战主要分为4部分:
- 创建索引
- 全量数据导入es
- 增量数据同步es
- 关键词检索
一、创建索引
博客的以下属性需要纳入检索:
| 字段 | 备注 | 属性 |
|---|---|---|
| id | ID | int(11) |
| title | 标题 | varchar(255) |
| description | 摘要 | varchar(255) |
| content | 内容 | text |
| category_id | 分类ID | int(11) |
| keyword_ids | 关键词 | varchar(255) |
| read_cnt | 阅读量 | int(11) |
| created_at | 发布时间 | TIMESTAMP |
| updated_at | 更新时间 | TIMESTAMP |
其中,title、description、content既需要分词来做全文检索,又需要保留部分原字符串便于直接搜索,所以使用fields将字段映射出不同类型:
"title": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
},而在分词器的选择上,为了既能对文档分词更细,又能对检索更精确,在对文档字段分词和对检索时的输入分词使用不同的分词器:
"title": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
},
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"search_analyzer": "ik_smart"
},比如,title为”重走丝绸之路“,ik_max_word分词如下:
{
"tokens": [
{
"token": "重走",
"start_offset": 0,
"end_offset": 2,
"type": "CN_WORD",
"position": 0
},
{
"token": "丝绸之路",
"start_offset": 2,
"end_offset": 6,
"type": "CN_WORD",
"position": 1
},
{
"token": "丝绸",
"start_offset": 2,
"end_offset": 4,
"type": "CN_WORD",
"position": 2
},
{
"token": "之路",
"start_offset": 4,
"end_offset": 6,
"type": "CN_WORD",
"position": 3
}
]
}而ik_smart分词粒度更粗:
{
"tokens": [
{
"token": "重走",
"start_offset": 0,
"end_offset": 2,
"type": "CN_WORD",
"position": 0
},
{
"token": "丝绸之路",
"start_offset": 2,
"end_offset": 6,
"type": "CN_WORD",
"position": 1
}
]
}键搜索词为”重走丝绸之路“,我们当然希望原文尽可能多匹配到这个检索词,而不是每个字都可能检索出一堆文档,这就是匹配的精确度。
对于keyword_ids、category_id,导入到es中时,就要装换成具体的内容了,才能要支持用户使用文本检索,而不是限制使用ID,这两个字段分别在es中字段名设置为keywords、category。
而且,一般来说关键词的检索,只考虑精确匹配,比如说关键词”全文检索“,如果要分词的话就会变成:
{
"tokens": [
{
"token": "全文",
"start_offset": 0,
"end_offset": 2,
"type": "CN_WORD",
"position": 0
},
{
"token": "检索",
"start_offset": 2,
"end_offset": 4,
"type": "CN_WORD",
"position": 1
}
]
}而实际上,全文可能匹配一部分文档,检索页匹配一部分文档,这对于关键词这个属性定义来说,是没有意义的,所以,我们对keywords、category使用”keyword“类型。
考虑到该实战只是最小实现,忽略别名(aliases),分片配置使用默认,相应的需建立索引articles如下:
{
"mappings": {
"doc": {
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "long"
},
"keywords": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
},
"categorys": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
},
"read_cnt": {
"type": "long"
},
"title": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
},
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"search_analyzer": "ik_smart"
},
"description": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
},
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"search_analyzer": "ik_smart"
},
"created_at": {
"type": "date",
"format": "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss||yyyy-MM-dd||epoch_millis"
},
"updated_at": {
"type": "date",
"format": "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss||yyyy-MM-dd||epoch_millis"
}
}
}
}
}使用 PUT /articles API创建索引成功后会返回:
{
"acknowledged": true,
"shards_acknowledged": true
}二、全量数据导入es
因为是对已有的博客网站打造全文检索,所以首先需要进行一次全量导入ES。第一步的操作都是直接使用es api完成的,而这一步涉及到数据查询与转换,则需要在我们的项目内完成。
首先我们需要熟悉es组件elasticsearch/elasticsearch的使用,以下介绍本次实战涉及到的一些功能,更多可以直接看文档:Elasticsearch-PHP 中文文档。
我们先在配置文件config/elastic.php定义好es的连接信息:
<?php
return array(
'default' => [
'hosts' => [
[
'host' => ‘xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx’,
'port' => '9200',
'scheme' => 'http',
]
],
'retries' => 1,
/*
|--------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Default Index Name
|--------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
| This is the index name that elasticquent will use for all
*/
'default_index' => ‘default_index’,
],
);
再使用批量批量索引文档的方法:bulk,示例:
for($i = 0; $i < 100; $i++) {
$params['body'][] = [
'index' => [
'_index' => 'my_index',
'_type' => 'my_type',
]
];
$params['body'][] = [
'my_field' => 'my_value'
];
}
$responses = ClientBuilder::create()->build()->bulk($params);
这里不能直接使用查库后的数据,需要做一些转换工作,比如keyword_ids 转换成keywords,我们封装一个函数:getDoc():
public function getDoc()
{
$fields = [
'id',
’title,
‘description’,
‘read_cnt’,
'created_at’,
‘updated_at’
];
$data = array_only($this->getAttributes(), $fields);
$data[‘keywords’] = ArticleKeyword::whereIn(‘id’, $this->keyword_ids)->pluck(‘name’)->toArray();
$data[‘category’] = ArticleCategory::find($this->category_id);
return $data;
}
直接调用该方法获取需要同步的文档数据。
注意使用该方法批量索引时,index + 一组数据是成对的。
按照第一步新建的索引,直接使用组件提供的批量索引功能全量将查询出的数据同步到es中。
3、增量数据同步es
对于新增的数据,需要在写入库中的同时同步到es,这里使用到的方案是Eloquent 的模型事件。
在 Eloquent 模型类上进行查询、插入、更新、删除操作时,会触发相应的模型事件,不管你有没有监听它们。这些事件包括:
retrieved 获取到模型实例后触发
creating 插入到数据库前触发
created 插入到数据库后触发
updating 更新到数据库前触发
updated 更新到数据库后触发
saving 保存到数据库前触发(插入/更新之前,无论插入还是更新都会触发)
saved 保存到数据库后触发(插入/更新之后,无论插入还是更新都会触发)
deleting 从数据库删除记录前触发
deleted 从数据库删除记录后触发
restoring 恢复软删除记录前触发
restored 恢复软删除记录后触发
而我们需要使用到的事件是:saved、deleted,监听这两个事件,在触发后同步到es,这样文章的增、改、删操作都能实时将数据变化同步到es。
我们使用fireModelEvent设置事件触发的同步操作,这里用到了组件中的单文档索引功能:index,示例:
$params = [
'index' => 'my_index',
'type' => 'my_type',
'id' => 'my_id',
'body' => [ 'testField' => 'abc']
];
$response = $client->index($params);使用第2步中的getDoc()方法来获取待更新的数据。
具体实现如下:
public function fireModelEvent($event, $halt = true)
{
if (in_array($event, ['saved', 'deleted']))
{
if($event == 'deleted')
{
ClientBuilder::create()->build()->delete(['id' => $this->id]);
}
if($event == 'saved')
{
$params = [
'index' => 'articles',
'type' => 'doc',
'id' => $this->id,
'body' => $this->getDoc()
];
ClientBuilder::create()->build()->index($params);
}
}
}4、检索数据
通过2、3步骤,我们的文章已经实时同步到es上了,这一步我们需要将es的全文检索开放给用户使用,在我的网站中,我在文章列表增加了一个搜索框给用户输入需检索的文本: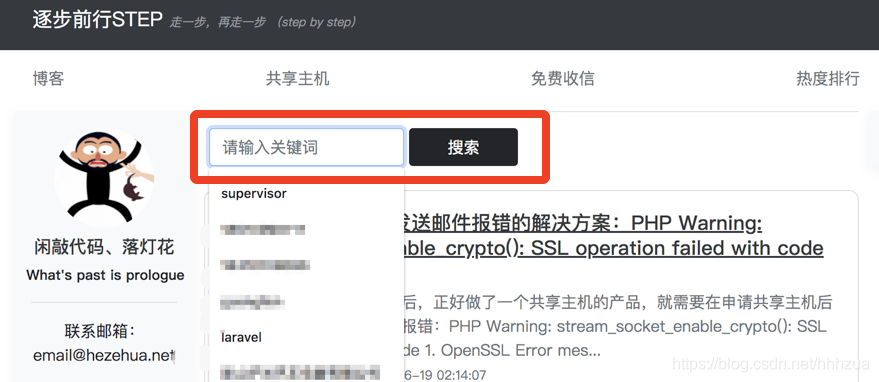
这里有两个需求:
1、对title、description、keywords、category 做 query_string 查询
2、将查询结果转化为Eloquent集合,便于结果展示
封装的检索函数:
public static function search($keyword, $page = 1, $per_page = 20, $conditions = [], $sort = null)
{
$page = max(1, intval($page));
$from = ($page - 1) * $per_page;
$query = [];
//搜索文本字段
$search_fields = ['title', 'keywords', 'category', 'description'];
if($keyword)
{
foreach ($search_fields as $key => $search_field)
{
$query['must']['bool']['should'][] = [
'query_string' => [
'default_field' => $search_field,
'query' => strtolower($keyword),
'default_operator' => 'AND',
]
];
}
}
$params = [
'index' => 'articles',
'type' => 'doc',
'body' => [
'query' => $query
]
];
$response = ClientBuilder::create()->build()->search($params);
$total_count = array_get($response, 'hits.total', 0);
$collection = new Collection();
foreach (array_get($response, 'hits.hits', []) as $key => $item)
{
$self = new static;
$self->setRawAttributes($item['_source'], true);
$collection->add($self);
}
return new LengthAwarePaginator($collection, $total_count, $per_page, intval($from/$per_page) + 1);
}